What Is Cost Per Click (CPC) in Google Ads?
Cost per click is the amount an advertiser pays each time a user clicks on their ad. This cost is influenced by the ad’s Quality Score, competition for keywords, industry, and other factors. CPC is central to understanding your Google Ads’ overall effectiveness because it affects the cost of reaching each potential customer.

In Google Ads, good CPC is determined during the ad auction, where Google considers each advertiser’s maximum bid and Quality Score (which measures relevance, quality, and expected performance). These factors influence the ad’s position on the search results page and the final CPC.
Factors That Influence Google Ads CPC
Several elements play a role in determining the CPC for a specific Google Ads campaign:
- Keyword Competition: Keywords with high search volume and strong competition often result in higher CPCs. For example, keywords in the legal, finance, and healthcare sectors are known for having some of the highest CPCs, as these industries are highly competitive and rely on valuable leads.
- Industry: Different industries have different CPC ranges, influenced by demand and ROI potential. High-CPC industries often include legal, finance, and insurance due to the lucrative nature of conversions in these fields.
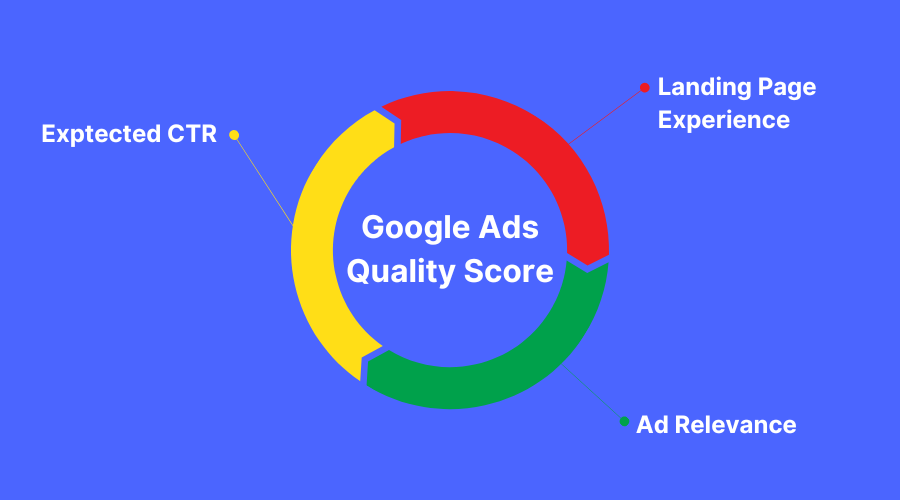
- Quality Score: Google rewards ads that are relevant and offer good user experiences with lower CPCs. Quality Score is determined by expected click-through rate (CTR), ad relevance, and landing page experience.
- Geographic Location: CPC varies by geographic location based on competition levels and audience demographics. Ads targeting highly populated cities or regions with strong purchasing power may cost more per click.
- Device Targeting: Desktop, mobile, and tablet CPCs can differ. In many cases, mobile CPCs are slightly lower than desktop, but this varies depending on the industry and audience behavior.
Average CPC Across Different Industries
Google Ads CPCs vary widely by industry due to differing levels of competition, conversion value, and advertiser demand. Here are some average CPCs across popular industries (note that these numbers are approximate and may change over time):
- Employment: $4.53
- Restaurant & Food: $2.18
- Traves: $1.92
- Education: $4.39
- Home Goods and Furniture: $6.96
- E-commerce: $1.16

For more up-to-date information on CPC across different industries, check out WordStream’s Google Ads Benchmarks, which regularly publishes insights on CPC and other key performance metrics.
Strategies to Lower CPC in Google Ads
While CPC can be high in competitive industries, there are several strategies advertisers can use to optimize their ads and lower their costs per click:
1. Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are more specific phrases with lower search volumes and typically less competition. By targeting long-tail keywords, advertisers can reach users with high intent to convert and often pay less per click than for more generic, competitive keywords.
2. Improve Your Quality Score
Quality Score directly influences CPC. Higher Quality Scores can reduce your CPC while boosting your ad position. To improve Quality Score:
- Optimize Ad Relevance: Align your ad copy closely with your target keywords.
- Enhance Landing Page Experience: Ensure that your landing page is relevant, loads quickly, and provides a good user experience.
- Increase Expected Click-Through Rate (CTR): Use compelling headlines and descriptions that encourage clicks.
3. Use Negative Keywords
Negative keywords prevent your ads from showing for searches that are unlikely to convert. For example, if you’re a paid software company, you might add “free” as a negative keyword to avoid clicks from users looking for free tools. Negative keywords help you avoid wasted spend, improve CTR, and can ultimately lower CPC by making your targeting more precise.
4. Leverage Geo-Targeting and Device Bids
Refine your targeting based on location and device. For example, if your audience is mainly in specific cities or states, focus your ad spend there. Similarly, use device bid adjustments to allocate more budget to devices that perform best, lowering costs by eliminating low-performing clicks.
5. Test and Optimize Ad Copy
Regularly test different versions of ad copy to see what resonates most with your audience. Use A/B testing to identify winning headlines, descriptions, and calls-to-action that drive higher CTR and relevance, which can positively impact Quality Score and CPC.
6. Consider Automated Bidding Strategies
If manual bidding is leading to high CPCs, you might explore automated bidding strategies like Target CPA (Cost Per Acquisition) or Maximize Conversions. These strategies allow Google’s algorithms to adjust bids in real-time based on the likelihood of conversion, which can help control CPC over time.
Monitoring CPC Over Time
CPC isn’t static, and it’s essential to monitor it consistently. Changes in keyword competition, seasonal trends, and adjustments to ad targeting can all impact CPC. Regularly check your Google Ads reports to identify trends in CPC and make proactive adjustments to bidding, targeting, or keyword strategy as needed.
Why Understanding CPC Matters for Your Google Ads Strategy
Understanding CPC isn’t just about managing costs—it’s about maximizing the effectiveness of every dollar spent on Google Ads. By analyzing industry CPC benchmarks, improving Quality Scores, and strategically targeting ads, businesses can make sure they’re getting the most value from their advertising budget. Lowering CPC without sacrificing reach or conversions can be transformative for ROI, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses.
For more guidance on how CPC fits into a broader Google Ads strategy, visit Google’s Official Guide to CPC, which provides an in-depth look at bidding strategies and Quality Score.
Last words
In summary, CPC is a foundational metric in Google Ads that can significantly affect the performance and cost-effectiveness of your campaigns. By focusing on Quality Score, keyword targeting, and ad optimization, you can reduce your CPC and make your Google Ads campaigns more efficient and profitable.
This understanding allows you to control advertising costs and generate more high-quality leads within your budget, leading to a stronger return on investment and sustained business growth.
