When businesses consider leveraging Google Ads to drive traffic and sales, one of the first questions that arises is: how much does Google Ads cost? The answer is multifaceted, influenced by several factors, and varies significantly depending on the industry, keywords, and goals. In this guide, we break down everything you need to know about the costs associated with Google Ads to help you make informed decisions and optimize your ad spend.
Understanding the Basics of Google Ads Pricing
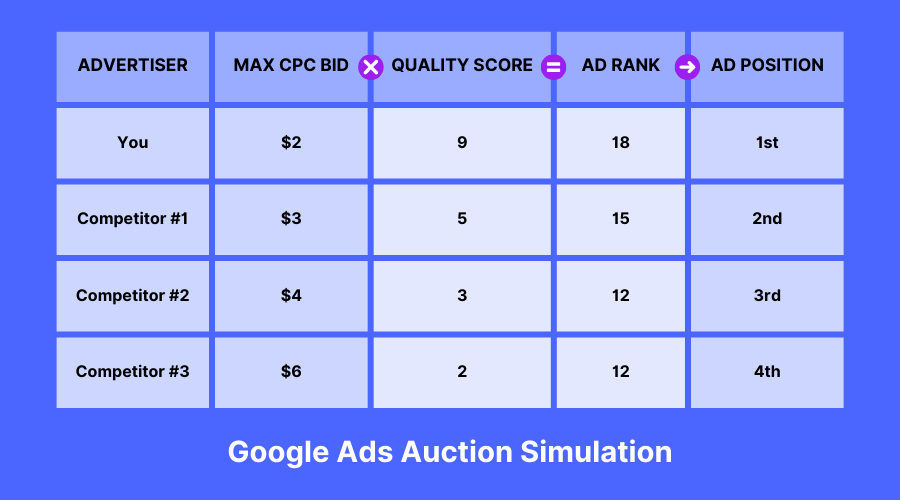
Google Ads operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, meaning advertisers pay only when users click on their ads. The pricing structure is determined through an auction system where advertisers bid on keywords relevant to their products or services. However, the highest bidder doesn’t always win the top position. Google also considers factors such as Quality Score and Ad Rank to determine the placement and cost of your ads.
What Is the Average Cost Per Click (CPC)?
The average cost per click on Google Ads typically ranges from $1 to $2 on the Google Search Network. However, this cost can be higher or lower depending on several factors:
- High-competition industries like legal services and insurance often see CPCs exceeding $50.
- Low-competition industries or niche markets may have CPCs under $1.
Understanding your industry’s average CPC is crucial for budgeting and performance forecasting.
How to Calculate Your Monthly Cost?
Google’s algorithm wants to count at least 10 clicks /day on your ads to have enough data to work with. Keeping this in mind, your are going to identify how much it would it cost you to get at least 12 clicks a day to be safe, for a whole month – using 30.5 days/month on average:
- List the keywords your are going to target
- Identify the Top of the Page CPC of each keyword
- Take the highest CPC of your list and multiply (x) it by 12
- Multiply (x) this new number by 30.5
Example: “Boat Rental Miami” – CPC = $3.96 X 12 (clicks) X 30.5 (days of the month) = $1,449 monthly media buy budget.
That way you get an estimate of how much it is going to cost you to run ads on Google for a given keyword. Now, this is absolutely not the exact budget you need to allocate to Google Ads. You can do really well with half of that estimate, maybe even less. It all depends on how many keywords you want to target and how good your ads are, you will read below that Google Ads is not just about bidding, ads quality score also matters.
Factors That Influence Google Ads Cost
Several variables affect the cost of running a Google Ads campaign. Let’s explore these factors in detail:
1. Keywords and Search Intent
Keywords are the foundation of Google Ads. High-demand keywords generally come with a higher cost due to increased competition.
- Short-tail keywords (e.g., “insurance”) are more expensive because of their broad targeting.
- Long-tail keywords (e.g., “affordable car insurance in New York”) tend to have lower CPCs and often attract more qualified leads.
Focusing on long-tail keywords can be a cost-effective strategy for small businesses.
2. Industry and Competition
The industry you operate in plays a significant role in determining your ad costs. For example:
- Legal and financial services have some of the highest CPCs, with keywords like “personal injury lawyer” reaching over $100 per click.
- E-commerce and retail sectors usually experience moderate CPCs, depending on product categories.
3. Quality Score
Google assigns a Quality Score to each ad based on its relevance, expected click-through rate (CTR), and landing page experience. In theory, when you have a higher Quality Score, that will lead to lower costs and better ad placements.
- Relevance of ad copy to the keyword.
- User experience on the landing page, including mobile-friendliness and page speed.
Improving Quality Score is a powerful way to reduce your Google Ads cost.
4. Geographic Targeting
Where you target your ads also influences cost. Advertising in highly populated and competitive regions generally incurs higher CPCs. Conversely, targeting smaller or less competitive locations can reduce your costs.
- Local campaigns targeting a specific city are often cheaper than nationwide campaigns.
5. Ad Scheduling
Running ads only during peak hours when your target audience is most active can help control spending and increase ROI.
- Ad scheduling allows advertisers to limit ads to specific days and times.
Types of Google Ads and Their Costs
Google Ads offers several ad formats, each with different pricing structures:
1. Search Ads
Search ads appear at the top of Google search results and are triggered by user queries. These ads are often the most expensive due to high intent and competition.
- Typical CPC range: $1 to $50, depending on keywords.
2. Display Ads
Display ads are being showned on websites within the Google Display Network. They have lower CPCs but are more suitable for building brand awareness than generating direct conversions.
- Typical CPC range: $0.30 to $3.
3. Shopping Ads
Shopping ads are used to feature and showcase product images, prices, and store information. They are highly effective for e-commerce businesses.
- Typical CPC range: $0.50 to $2.
4. Video Ads
Video ads run on YouTube and other video platforms. Pricing is often based on cost per view (CPV).
- Typical CPV range: $0.10 to $0.30.
5. App Promotion Ads
These ads promote app installations and engagement. Costs depend on your bidding strategy (CPC, cost-per-install, etc.).
How to Optimize Your Google Ads Budget
Controlling costs while maximizing performance requires strategic planning. Here are some best practices:
1. Use Negative Keywords
Negative keywords prevent your ads from showing for irrelevant searches, reducing wasted spend.
- Example: Adding “free” as a negative keyword if you sell premium software.
Here is a good guide on how to use negative keywords.
2. Refine Your Targeting
Narrow your audience based on location, demographics, and device preferences to focus your budget where it matters most.
3. Set Bid Adjustments
Bid adjustments allow you to increase or decrease bids for specific conditions, such as mobile devices or peak hours.
- Example: Increase bids during business hours when conversions are higher.
4. Monitor and Adjust Campaigns Regularly
Frequent monitoring ensures you catch underperforming ads and adjust accordingly.
- Use Google Ads reports to track performance and identify cost-saving opportunities and weaknesses in metrics like high CPC, low CTR, high Cost Per Conversion etc.
- Improve your ad copy regularly to doing A/B Tests, to make sure you are using the best version of your ads.
Conclusion
The cost of Google Ads varies widely based on your industry, keyword strategy, and targeting. By understanding the factors that influence pricing and implementing smart optimization strategies, you can achieve a better return on investment.
FAQ – How Much Does Google Ads Cost
How much should I budget for Google Ads?
Your Google Ads budget depends on your industry, competition, and marketing goals. Small businesses often start with $500 to $1,000 per month and scale up based on performance.
Are Google Ads worth the cost?
Yes, Google Ads can be highly effective if managed correctly. It allows precise targeting, immediate visibility, and measurable results, making it a valuable investment for many businesses.
What is a good CPC for Google Ads?
A good CPC depends on your industry and profit margins. Generally, keeping CPC below $2 for broad keywords and below $1 for niche keywords is ideal, but this varies by sector.
Can I run Google Ads with a limited budget?
Yes, you can set daily and overall campaign limits to manage your ad spend. Focusing on long-tail keywords and refining targeting can help maximize results within a smaller budget.
How do I lower my Google Ads cost?
Improving Quality Score, using negative keywords, refining targeting, and optimizing ad copy are effective ways to reduce costs.